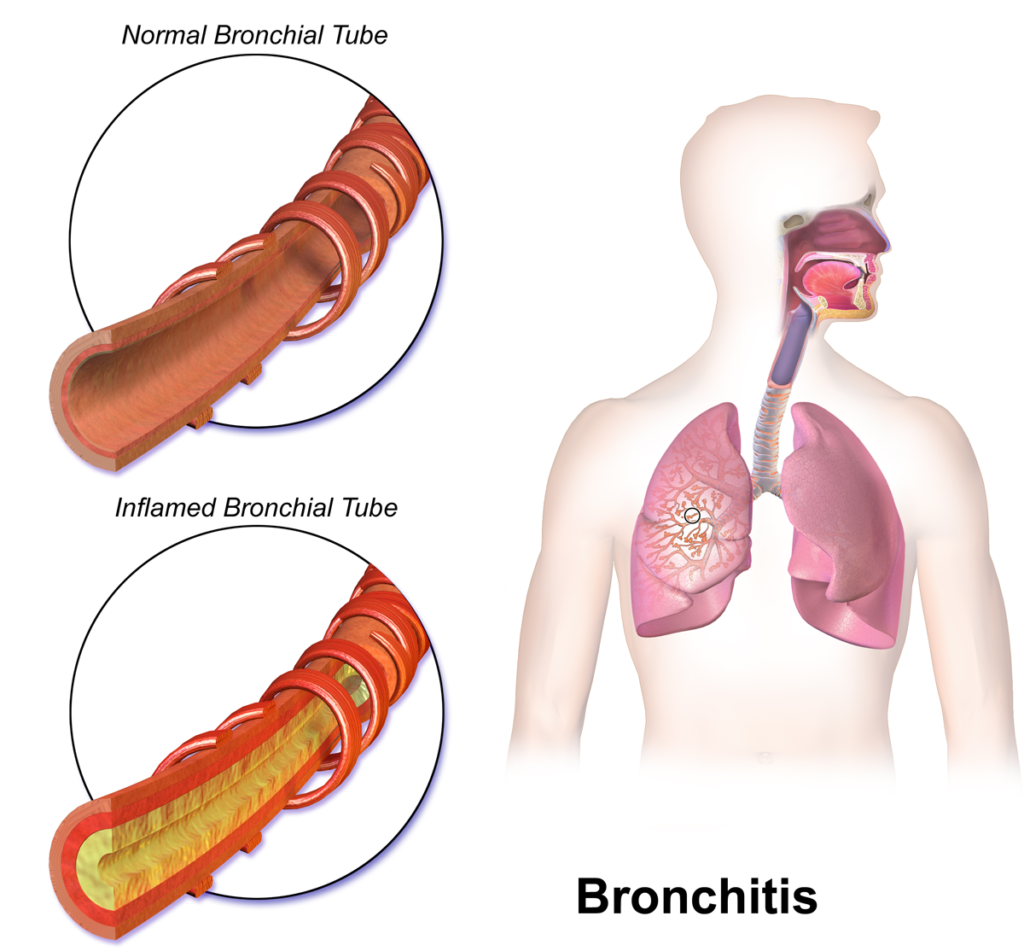
Introduction to Bronchitis
Bronchitis is a common respiratory disease characterized by inflammation of the bronchial tubes, the airways that carry oxygen to the lungs. There are two main types of bronchitis: acute and chronic. Acute bronchitis is usually a short-term illness following a viral respiratory infection. It typically improves on its own without long-term effects. On the other hand, chronic bronchitis is a long-term condition that often results from prolonged exposure to irritants such as tobacco smoke or air pollution. It requires ongoing medical attention and can significantly impact a person’s quality of life.
Causes of Bronchitis
The primary causes of bronchitis are infections and environmental factors. Infections leading to bronchitis are typically viral, but bacterial infections can also cause the condition. Common viruses that can lead to bronchitis include influenza (flu), common cold, and respiratory syncytial virus (RSV). Environmental factors play a significant role in the development of chronic bronchitis. These include exposure to tobacco smoke, air pollution, dust, and certain chemicals. According to the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI), individuals with frequent exposure to these irritants are at a higher risk of developing chronic bronchitis.
Symptoms of Bronchitis
The symptoms of bronchitis can vary significantly depending on whether the condition is acute or chronic. However, some common symptoms include:
- Persistent cough
- Production of mucus, which can be clear, white, yellowish-gray, or green
- Fatigue
- Shortness of breath
- Mild fever and chills
- Chest discomfort
In acute bronchitis, these symptoms are often more severe but typically resolve within a few weeks. However, in chronic bronchitis, symptoms are usually milder but persist for a long time. Chronic bronchitis is characterized by a productive cough that lasts for at least three months, with recurring bouts occurring for at least two consecutive years. The Mayo Clinic provides a comprehensive list of symptoms for both types of bronchitis.
Diagnosis of Bronchitis
The diagnosis of bronchitis typically begins with a thorough review of the patient’s medical history and a physical examination. During the physical exam, the doctor will listen to the patient’s lungs with a stethoscope to check for any abnormal sounds that might indicate bronchitis.
Common diagnostic methods include:
- Chest X-ray: This can help the doctor rule out other lung conditions that might cause similar symptoms, such as pneumonia.
- Sputum tests: If the patient is producing phlegm, it can be tested to determine the cause of the infection.
- Pulmonary function test: This involves the patient blowing into a device called a spirometer, which measures how much air the lungs can hold and how quickly one can expel air from the lungs.
The importance of early diagnosis cannot be overstated. Early diagnosis of bronchitis can help manage the symptoms more effectively, prevent potential complications, and improve the patient’s quality of life. According to the Cleveland Clinic, chronic bronchitis, if left undiagnosed or untreated, can lead to serious conditions such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) or heart failure.
Treatment of Bronchitis
The treatment of bronchitis primarily aims to relieve symptoms, improve breathing, and manage any underlying cause. Common treatments include:
- Rest and hydration: These are crucial for recovery from any illness, including bronchitis.
- Cough suppressants: These can help if the cough is severe and causing discomfort or preventing sleep.
- Pain relievers: These can help alleviate muscle aches, fever, and headaches.
- Bronchodilators: These can help open up the bronchial tubes and clear out mucus.
- Pulmonary rehabilitation: This is a program of exercise, disease management, and counseling aimed at improving lung health.
The treatment approach can differ between acute and chronic bronchitis. Acute bronchitis often resolves on its own, and treatment primarily focuses on relieving symptoms. On the other hand, chronic bronchitis often requires long-term management strategies such as quitting smoking, avoiding irritants, and taking prescribed medications to control symptoms and improve lung function. The National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI) provides comprehensive information on the treatment of bronchitis.
Chronic Bronchitis
Chronic bronchitis is a type of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) characterized by a long-term productive cough. It’s defined by having a cough and sputum production for at least three months in two consecutive years. Chronic bronchitis is primarily caused by long-term exposure to irritants that damage the lungs and the airways. The most common irritant is cigarette smoke, but others include air pollution, chemical fumes, and dust.
Chronic bronchitis can have significant long-term effects on the body. Over time, the inflammation in the bronchial tubes leads to scarring, narrowing, and thickening of the airways. This can make breathing difficult and cause a feeling of breathlessness. Chronic bronchitis can also lead to decreased oxygen levels in the blood, leading to fatigue and other health problems over time. In severe cases, chronic bronchitis can lead to respiratory failure, a serious condition where the lungs can’t provide the body with enough oxygen. According to the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI), managing chronic bronchitis is crucial to prevent these complications and improve the quality of life.
Acute Bronchitis
Acute bronchitis, also known as a chest cold, is a short-term inflammation of the bronchial tubes. It’s most often caused by a viral infection, such as the common cold or the flu, but can also be caused by bacterial infections or exposure to irritants like tobacco smoke. Unlike chronic bronchitis, acute bronchitis usually resolves on its own within a few weeks.
The symptoms of acute bronchitis can be similar to those of chronic bronchitis, including a persistent cough, production of mucus, fatigue, shortness of breath, and chest discomfort. However, these symptoms are usually more severe but last for a shorter period.
The key difference between acute and chronic bronchitis lies in the duration and the cause of the condition. Acute bronchitis is a temporary condition that often follows a viral respiratory infection, while chronic bronchitis is a long-term condition that’s most often caused by long-term exposure to lung irritants, especially cigarette smoke. The Mayo Clinic provides a comprehensive comparison of acute and chronic bronchitis.
Prevention
Preventing bronchitis, especially chronic bronchitis, is largely about avoiding the irritants that can cause damage to your lungs and airways. Here are some tips for preventing bronchitis:
- Quit smoking: Smoking is the leading cause of chronic bronchitis. Quitting smoking is the most important step you can take to prevent bronchitis.
- Avoid secondhand smoke: Secondhand smoke can also damage your lungs and increase your risk of bronchitis.
- Avoid air pollution: Try to limit your exposure to air pollution as much as possible. On days when air quality is poor, try to stay indoors.
- Wear a mask: If you can’t avoid exposure to dust or chemical fumes, wear a mask to protect your lungs.
- Get vaccinated: Regular vaccinations can help prevent viral infections that can lead to acute bronchitis.
The importance of prevention cannot be overstated. Preventing bronchitis can help you avoid the discomfort of its symptoms and the potential complications associated with chronic bronchitis. According to the Cleveland Clinic, prevention is a crucial part of managing lung health and preventing chronic respiratory diseases.
Living with Bronchitis
Living with bronchitis, especially chronic bronchitis, can be challenging. However, with the right management strategies, you can control your symptoms and improve your quality of life. Here are some tips for managing bronchitis:
- Follow your treatment plan: If you’ve been prescribed medication or other treatments, it’s important to follow your doctor’s instructions closely.
- Stay active: Regular physical activity can help strengthen your respiratory muscles and improve your overall lung function.
- Eat a healthy diet: A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains can help boost your immune system and keep your body strong.
- Manage stress: High levels of stress can worsen your bronchitis symptoms. Techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, and yoga can help manage stress levels.
In addition to these management strategies, making certain lifestyle changes can also help manage bronchitis. These may include quitting smoking, avoiding lung irritants, and getting regular exercise. The National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI) provides comprehensive information on living with bronchitis and managing symptoms.
FAQ Section
Q: What are the 3 symptoms of bronchitis?
A: The three common symptoms of bronchitis are a persistent cough, production of mucus, and fatigue. However, symptoms can vary depending on whether the bronchitis is acute or chronic.
Q: What is the best thing to do for bronchitis?
A: The best thing to do for bronchitis is to follow your doctor’s treatment plan, which may include rest, hydration, cough suppressants, and in some cases, antibiotics. The Mayo Clinic provides comprehensive information on managing bronchitis.
Q: What are 5 symptoms of bronchitis?
A: Five symptoms of bronchitis can include a persistent cough, production of mucus, fatigue, shortness of breath, and chest discomfort. Symptoms can vary depending on the type of bronchitis (acute or chronic).
Q: How contagious is bronchitis?
A: Acute bronchitis, often caused by a viral infection, can be contagious. Chronic bronchitis, usually caused by long-term exposure to lung irritants like tobacco smoke, is not contagious. The Cleveland Clinic provides more information on this topic.
Conclusion
In conclusion, bronchitis is a common respiratory condition that can significantly impact a person’s quality of life, especially if it becomes chronic. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for bronchitis is crucial for managing the condition effectively.
Prevention strategies, such as avoiding lung irritants and getting regular vaccinations, can help reduce the risk of developing bronchitis. If you’re living with bronchitis, following your treatment plan and making certain lifestyle changes can help manage your symptoms and improve your quality of life.
Remember, if you have persistent symptoms of bronchitis, it’s important to seek medical attention. Early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent complications and improve your overall health. For more information on bronchitis, visit resources like the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI) or the Mayo Clinic.